Location
CoLab, COM 100
Start Date
1-5-2025 5:30 PM
Document Type
Poster
Description
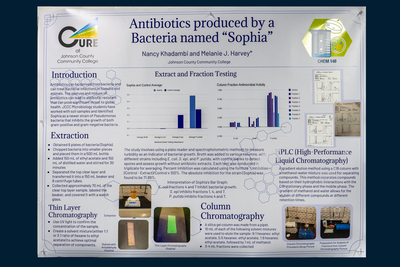
Antibiotics can be derived from bacteria and can treat bacterial infections in humans and animals. The overuse and misuse of antibiotics can lead to antibiotic resistant that can pose significant threat to global health. JCCC Microbiology students have worked with soil samples and identified Sophia as a newer strain of Pseudomonas bacteria that inhibits the growth of both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. In this research we extracted and tested antibiotics produced by Sophia (Bacteria). Chemical extracts taken from bacteria named Sophia inhibit both, E. coli and S. epi when grown in broth with the extract. We used chromatography to separate the extract mixture, including TLC (Thin-Layer Chromatography), Column chromatography, and HPLC (high performance liquid chromatography) to separate the extract mixtures. After each step in the process, the fractions were tested against strains in broth using a plate reader.
Antibiotics Produced by a Bacteria named “Sophia”
CoLab, COM 100
Antibiotics can be derived from bacteria and can treat bacterial infections in humans and animals. The overuse and misuse of antibiotics can lead to antibiotic resistant that can pose significant threat to global health. JCCC Microbiology students have worked with soil samples and identified Sophia as a newer strain of Pseudomonas bacteria that inhibits the growth of both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. In this research we extracted and tested antibiotics produced by Sophia (Bacteria). Chemical extracts taken from bacteria named Sophia inhibit both, E. coli and S. epi when grown in broth with the extract. We used chromatography to separate the extract mixture, including TLC (Thin-Layer Chromatography), Column chromatography, and HPLC (high performance liquid chromatography) to separate the extract mixtures. After each step in the process, the fractions were tested against strains in broth using a plate reader.

Comments
The faculty mentor for this project was Melanie Harvey, Chemistry.